Guadeloupe topographic map
Interactive map
Click on the map to display elevation.
Guadeloupe
The main two islands are Basse-Terre (west) and Grande-Terre (east), which form a butterfly shape as viewed from above, the two 'wings' of which are separated by the Grand Cul-de-Sac Marin, Rivière Salée and Petit Cul-de-Sac Marin. More than half of Guadeloupe's land surface consists of the 847.8 km2 Basse-Terre. The island is mountainous, containing such peaks as Mount Sans Toucher (4,442 feet; 1,354 metres) and Grande Découverte (4,143 feet; 1,263 metres), culminating in the active volcano La Grande Soufrière, the highest mountain peak in the Lesser Antilles with an elevation of 1,467 metres (4,813 ft). In contrast Grande-Terre is mostly flat, with rocky coasts to the north, irregular hills at the centre, mangrove at the southwest, and white sand beaches sheltered by coral reefs along the southern shore. This is where the main tourist resorts are found.
About this map
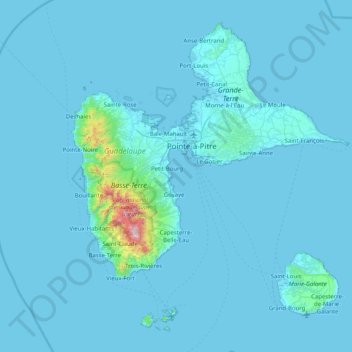
Name: Guadeloupe topographic map, elevation, terrain.
Location: Guadeloupe, France (15.83198 -61.80976 16.51448 -61.00130)
Average elevation: 37 m
Minimum elevation: -1 m
Maximum elevation: 1,442 m
Other topographic maps
Click on a map to view its topography, its elevation and its terrain.
Paris
France > Ile-de-France > Paris
Paris in its early history had only the rivers Seine and Bièvre for water. From 1809, the Canal de l'Ourcq provided Paris with water from less-polluted rivers to the north-east of the capital. From 1857, the civil engineer Eugène Belgrand, under Napoleon III, oversaw the construction of a series of new…
Average elevation: 62 m
Le Rhône - Bras Mort de la Barthelasse
France > Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur > Vaucluse > Avignon
Average elevation: 24 m
Grenoble
France > Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes > Isère
Except for a few dozen houses on the slopes of the Bastille hill of Chartreuse, Grenoble is exclusively built on the alluvial plain of the rivers Isère and Drac at an altitude of 214 metres (702 ft). As a result, the city itself is extremely flat. Mountain sports are an important tourist attraction in summer…
Average elevation: 246 m
Ardennes
Covering 5,229 square kilometres (2,019 square miles), the department was the smallest among the four contributors to Champagne-Ardenne. It is diverse in climate, topography, natural vegetation and land use, which is a mixture of forest and arable farming.
Average elevation: 225 m
Chamonix-Mont-Blanc
France > Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes > Upper Savoy
Due to its elevation, Chamonix has a humid continental climate (Dfb, according to the Köppen climate classification), with an average annual precipitation of 1,280 mm (50 in). Summers are mild and winters are cold and snowy.
Average elevation: 2,215 m
Annecy
France > Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes > Annecy
Annecy has an oceanic climate (Köppen Cfb) in spite of its relatively far inland position. Influenced by its elevation, summers are rather moderate on average, although they can be highly variable with extreme heat spikes. Winters see occasional freezing temperatures, but most often stays in the single-digits…
Average elevation: 554 m
Brittany
France > Brittany > Landerneau > Loudéac
The Armorican massif reaches its maximal elevation outside of Brittany, in neighbouring Mayenne, at 417 m, and slopes towards the west before straightening on its western extremity, with the Montagnes Noires and the Monts d'Arrée. The highest hill in Brittany is the Roc'h Ruz in the Monts d'Arrée, at 385 m…
Average elevation: 50 m
Rhone
The Rhône begins as the meltwater of the Rhône Glacier in Valais, in the Swiss Alps, at an altitude of approximately 2,208 metres (7,244 ft). From there it flows southwest through Gletsch and the Goms, the uppermost valley region of the Valais before Brig. In the Brig area, it receives the waters of the…
Average elevation: 842 m
Toulouse
France > Occitania > Haute-Garonne
The first half of the 14th century was a prosperous period, despite the dismemberment in 1317 of the very large bishopric of Toulouse (which lost two thirds of its area and a large part of its income, a loss only partially compensated by its elevation to the rank of archbishopric), and the episode of the…
Average elevation: 155 m
Argentière
France > Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes > Upper Savoy > Chamonix-Mont-Blanc
Argentière (French pronunciation: [aʁʒɑ̃tjɛʁ]) is a picturesque skiing, alpine walking and mountaineering village in the French Alps, part of the commune of Chamonix-Mont-Blanc, at an altitude of 1,252 m (4,108 ft).
Average elevation: 1,674 m
Corsica
Under the Köppen climate classification scheme, coastal regions are characterized by a hot-summer Mediterranean climate (Csa). Further inland, a warm-summer Mediterranean climate (Csb) is more common. At the highest elevation locations, small areas with a subarctic climate (Dsc, Dfc) and the rare cold-summer…
Average elevation: 139 m
Mont Blanc / Monte Bianco
France > Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes > Upper Savoy > Saint-Gervais-les-Bains
The climate is cold and temperate (Köppen climate classification Cfb), and is greatly influenced by altitude. Being the highest part of the Alps, Mont Blanc and surrounding mountains can create their own weather patterns. Temperatures drop as the mountains gain in height, and the summit of Mont Blanc is a…
Average elevation: 4,092 m
Akamaru
Akamaru is the third largest island in the Gambier Islands of French Polynesia. It is a small, rocky island with an area of approximately 2.6 km2 (1.0 sq mi). The island is located approximately 7 km (4.3 mi) southeast of Mangareva, which is the largest island of the whole Gambier Islands archipelago.…
Average elevation: 15 m
