Mainz topographic map
Interactive map
Click on the map to display elevation.
Mainz
Nevertheless, the post-war reconstruction took place very slowly. While cities such as Frankfurt had been rebuilt fast by a central authority, only individual efforts were initially successful in rebuilding Mainz. The reason for this was that the French wanted Mainz to expand and become a model city. Mainz lay within the French-controlled sector of Germany and it was a French architect and town-planner, Marcel Lods, who produced a Le Corbusier-style plan of an ideal architecture. But the very first interest of the inhabitants was the restoration of housing areas. Even after the failure of the model city plans it was the initiative of the French (founding of the Johannes Gutenberg University of Mainz, elevation of Mainz to the state capital of Rhineland-Palatinate, the early resumption of the Mainz carnival) driving the city in a positive development after the war. The City Plan of 1958 by Ernst May allowed a regulated reconstruction for the first time. In 1950, the seat of the government of Rhineland-Palatinate had been transferred to the new Mainz and in 1963 the seat of the new ZDF, notable architects were Adolf Bayer, Richard Jörg and Egon Hartmann. At the time of the two-thousand-years-anniversary in 1962 the city was largely reconstructed. During the 1950s and 1960s, the Oberstadt had been extended, Münchfeld and Lerchenberg added as suburbs, the Altstadttangente (intersection of the old town), new neighbourhoods as Westring and Südring contributed to the extension. By 1970 there remained only a few ruins. The new town hall of Mainz had been designed by Arne Jacobsen and finished by Dissing+Weitling. The town used Jacobsens activity for the Danish Novo erecting a new office and warehouse building to contact him. The urban renewal of the old town changed the inner city. In the framework of the preparation of the cathedrals millennium, pedestrian zones were developed around the cathedral, in northern direction to the Neubrunnenplatz and in a southern direction across the Leichhof to the Augustinerstraße and Kirschgarten. The 1980s brought the renewal of the façades on the Markt and a new inner-city neighbourhood on the Kästrich. During the 1990s the Kisselberg between Gonsenheim and Bretzenheim, the "Fort Malakoff Center" at the site of the old police barracks, the renewal of the Main Station and the demolition of the first post-war shopping centre at the Markt followed by the erection of a new historicising building at the same place.
About this map
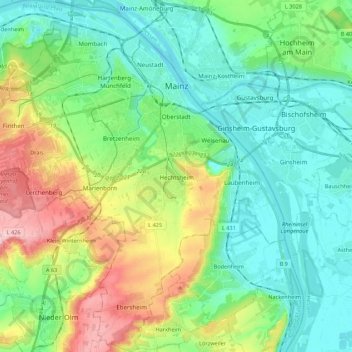
Name: Mainz topographic map, elevation, terrain.
Location: Mainz, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany (49.89553 8.14309 50.03530 8.34314)
Average elevation: 132 m
Minimum elevation: 79 m
Maximum elevation: 261 m
Other topographic maps
Click on a map to view its topography, its elevation and its terrain.
Schönenberg
Germany > Rhineland-Palatinate > Landkreis Kusel > Schönenberg-Kübelberg
Average elevation: 266 m
Reiferscheid
Germany > Rhineland-Palatinate > Landkreis Altenkirchen (Westerwald)
Average elevation: 240 m
Nürburg
Germany > Rhineland-Palatinate > Landkreis Ahrweiler
Nürburg has a semi-continental climate with both oceanic and continental tendencies. It does however land in the former category (Köppen Cfb). With regards to the racetrack, due to the Nordschleife's varied terrain and elevation, weather may be completely different on either end of the track. The elevation…
Average elevation: 560 m
Hochstadt (Pfalz)
Germany > Rhineland-Palatinate > Landkreis Südliche Weinstraße
Average elevation: 133 m
Horhausen (Westerwald)
Germany > Rhineland-Palatinate > Landkreis Altenkirchen (Westerwald)
Average elevation: 310 m
Weiperath
Germany > Rhineland-Palatinate > Landkreis Bernkastel-Wittlich > Morbach
The municipality lies at an elevation of between 430 and 770 m above sea level in the low mountain range of the Hunsrück on the boundary with the Birkenfeld district, roughly 25 km southeast of Wittlich and 35 km east of Trier. Its population is 11,051. The nearest town is Bernkastel-Kues.
Average elevation: 439 m
Altenglan
Germany > Rhineland-Palatinate > Landkreis Kusel
The municipality lies in the uplands in the Western Palatinate on the river Glan, which is the village's namesake, at an elevation in the valley of some 200 m above sea level, although the elevations within municipal limits reach almost 400 m (Bistersberg 387 m on the Glan's left bank; Kalmet 390 m on the…
Average elevation: 305 m
Air Base
Germany > Rhineland-Palatinate > Landkreis Kaiserslautern > Ramstein-Miesenbach
Average elevation: 237 m
Wolf
Germany > Rhineland-Palatinate > Landkreis Bernkastel-Wittlich > Traben-Trarbach
Average elevation: 201 m
Dünebusch
Germany > Rhineland-Palatinate > Landkreis Altenkirchen (Westerwald) > Bitzen
Average elevation: 206 m
Deidesheim
Germany > Rhineland-Palatinate > Landkreis Bad Dürkheim
From a local climatic point of view, Deidesheim is part of the climatically favoured foothill zone of the Weinstraße region. With a mean elevation of 235 m above sea level at the forest's edge, the lands of the Deidesheim area reach down to some 130 m above sea level at the lower mid-slope area in the…
Average elevation: 194 m
Idar-Oberstein
Germany > Rhineland-Palatinate > Landkreis Birkenfeld
Idar-Oberstein/Göttschied Airfield lies north of the town between the constituent community of Göttschied and the municipalities of Gerach and Hintertiefenbach at an elevation of 480 m above sea level (1,575 feet). Its ICAO location indicator is EDRG. The grass landing strip's orientation is 06/24, and it is…
Average elevation: 406 m
Feusdorf
Germany > Rhineland-Palatinate > Landkreis Vulkaneifel
Feusdorf's area is 442 ha all together, of which cropfields and open water make up 78 ha, greenbelt and heath 203 ha, private property 26 ha, woods 105 ha, public roadways 26 ha and other lands 4 ha. Flurbereinigung was undertaken in 1968. Feusdorf lies at an elevation of 450 to 565 m above sea level.
Average elevation: 503 m
