Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Guadeloupe topographic map
Click on the map to display elevation.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Guadeloupe
The main two islands are Basse-Terre (west) and Grande-Terre (east), which form a butterfly shape as viewed from above, the two 'wings' of which are separated by the Grand Cul-de-Sac Marin, Rivière Salée and Petit Cul-de-Sac Marin. More than half of Guadeloupe's land surface consists of the 847.8 km2 Basse-Terre. The island is mountainous, containing such peaks as Mount Sans Toucher (4,442 feet; 1,354 metres) and Grande Découverte (4,143 feet; 1,263 metres), culminating in the active volcano La Grande Soufrière, the highest mountain peak in the Lesser Antilles with an elevation of 1,467 metres (4,813 ft). In contrast Grande-Terre is mostly flat, with rocky coasts to the north, irregular hills at the centre, mangrove at the southwest, and white sand beaches sheltered by coral reefs along the southern shore. This is where the main tourist resorts are found.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
About this map
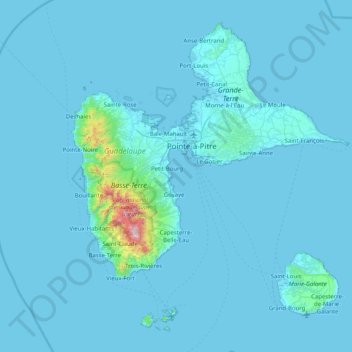
Name: Guadeloupe topographic map, elevation, terrain.
Location: Guadeloupe, France (15.83198 -61.80976 16.51448 -61.00130)
Average elevation: 37 m
Minimum elevation: -1 m
Maximum elevation: 1,442 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Other topographic maps
Click on a map to view its topography, its elevation and its terrain.
La Feuillarde
France > Centre-Val de Loire > Indre-et-Loire > Saint-Pierre-des-Corps
Average elevation: 55 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Revest
France > Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur > Alpes-de-Haute-Provence > Malijai
Average elevation: 524 m
Bionnay
France > Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes > Upper Savoy > Saint-Gervais-les-Bains
Average elevation: 1,276 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Lotissement Le Clos de Kersioual
France > Brittany > Finistère > Port-la-Forêt
Average elevation: 25 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Les Aravis d'en Bas
France > Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes > Upper Savoy > La Clusaz
Average elevation: 1,649 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
La Ligotière
France > Normandy > Manche > Villedieu-les-Poêles-Rouffigny > Villedieu-les-Poêles
Average elevation: 162 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
La Chervinière
France > Pays de la Loire > Vendée > Rives-du-Fougerais > Saint-Sulpice-en-Pareds
Average elevation: 87 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Orcières-Merlette
France > Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur > Hautes-Alpes > Orcières
Average elevation: 1,874 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
La Graissière
France > Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes > Puy-de-Dôme > Saint-Genès-Champanelle
Average elevation: 984 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Le Plan de l'Envers
France > Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes > Upper Savoy > Vallorcine
Average elevation: 1,721 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Le Champtier des Fourneaux
France > Ile-de-France > Yvelines > Dampierre-en-Yvelines
Average elevation: 143 m
Château Cos d'Estournel
France > Nouvelle-Aquitaine > Gironde > Saint-Estèphe > Cos
Average elevation: 14 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Barre des Écrins
France > Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur > Hautes-Alpes > Vallouise-Pelvoux
The Barre des Écrins (French pronunciation: [baʁ dez‿ekʁɛ̃]) is a mountain in the French Alps with a peak elevation of 4,102 metres (13,458 ft). It is the highest peak of the Massif des Écrins and the Dauphiné Alps and the most southerly alpine peak in Europe that is higher than 4,000 metres. It is…
Average elevation: 3,222 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Mont Blanc / Monte Bianco
France > Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes > Upper Savoy > Saint-Gervais-les-Bains
The climate is cold and temperate (Köppen climate classification Cfb), and is greatly influenced by altitude. Being the highest part of the Alps, Mont Blanc and surrounding mountains can create their own weather patterns. Temperatures drop as the mountains gain in height, and the summit of Mont Blanc is a…
Average elevation: 4,092 m
Falkenstein Castle
France > Grand Est > Moselle > Philippsbourg
In 1981, the Vosges Club (club vosgien) in Strasbourg placed a marker at the castle summit showing the altitude and directions to nearby land features.
Average elevation: 269 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Terres du Gd Sous Les Vign
France > Centre-Val de Loire > Loiret > Dordives > Le Grand-sous-les-Vignes
Average elevation: 93 m
Val Thorens
France > Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes > Savoy
Val Thorens ([val tɔʁɑ̃]) is a ski town in the Tarentaise Valley in the French Alps at an altitude of 2,300 m (7,500 ft). It is located in the commune of Saint-Martin-de-Belleville in the Savoie department. The resort forms part of the Les Trois Vallées ski area which, with over 600 km of slopes, is one…
Average elevation: 2,516 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
