Nablus topographic map
Interactive map
Click on the map to display elevation.
Nablus
Insofar as the hilly topography of the site would allow, the city was built on a Roman grid plan and settled with veterans who fought in the victorious legions and other foreign colonists. In the 2nd century CE, Emperor Hadrian built a grand theater in Neapolis that could seat up to 7,000 people. Coins found in Nablus dating to this period depict Roman military emblems and gods and goddesses of the Greek pantheon such as Zeus, Artemis, Serapis, and Asklepios. Neapolis was entirely pagan at this time. Justin Martyr who was born in the city c. 100 CE, came into contact with Platonism, but not with Christians there. The city flourished until the civil war between Septimius Severus and Pescennius Niger in 198–9 CE. Having sided with Niger, who was defeated, the city was temporarily stripped of its legal privileges by Severus, who designated these to Sebastia instead.
About this map
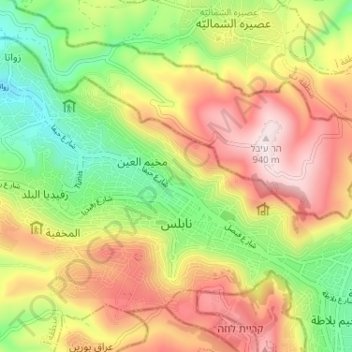
Name: Nablus topographic map, elevation, terrain.
Location: Nablus, Area A, West Bank, Palestinian Territories (32.20713 35.21811 32.24819 35.28262)
Average elevation: 645 m
Minimum elevation: 374 m
Maximum elevation: 938 m
Other topographic maps
Click on a map to view its topography, its elevation and its terrain.
Bethlehem
Palestinian Territories > Area A > Bethlehem
Bethlehem is located at an elevation of about 775 meters (2,543 ft) above sea level, 30 meters (98 ft) higher than nearby Jerusalem. Bethlehem is situated on the Judean Mountains.
Average elevation: 553 m
Jenin
Palestinian Territories > Area A
Jenin is situated at the foot of the rugged northernmost hills (Jabal Nablus) of the West Bank, and along the southern edge of the Jezreel Valley (Marj Ibn Amer),[65] which the city overlooks.[66] Its highest elevation is about 250 meters above sea level and its lowest areas are 90 meters above sea level.[67]…
Average elevation: 223 m
