West Bengal topographic map
Interactive map
Click on the map to display elevation.
West Bengal
The distribution of vegetation in northern West Bengal is dictated by elevation and precipitation. For example, the foothills of the Himalayas, the Dooars, are densely wooded with sal and other tropical evergreen trees. Above an elevation of 1,000 metres (3,300 ft), the forest becomes predominantly subtropical. In Darjeeling, which is above 1,500 metres (4,900 ft), temperate forest trees like oaks, conifers and rhododendrons predominate.
About this map
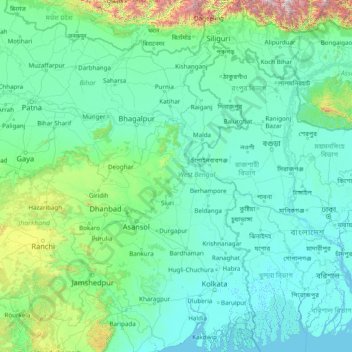
Name: West Bengal topographic map, elevation, terrain.
Location: West Bengal, India (21.54730 85.81967 27.22107 89.88260)
Average elevation: 182 m
Minimum elevation: -2 m
Maximum elevation: 4,101 m
Other topographic maps
Click on a map to view its topography, its elevation and its terrain.
Vijayawada
Vijayawada lies on the banks of Krishna river, covered by hills and canals. and at an altitude of 11 m (36 ft) above sea level. Three canals originating from the north side of the Prakasam Barrage reservoir — Eluru, Bandar, and Ryves — flow through the city.
Average elevation: 37 m
Navi Mumbai
India > Maharashtra > Thane > Navi Mumbai
Navi Mumbai (Marathi pronunciation: , also known by its former name New Bombay), is a planned city off the west coast of the Indian state of Maharashtra in Konkan division. The city is divided into two parts, North Navi Mumbai and South Navi Mumbai, for the individual development of Panvel Mega City, which…
Average elevation: 30 m
Guwahati
Professor Abani Kumar Bhagawati of Gauhati University stated that since before there were sufficient wetlands to absorb rainwater and channels to carry excess water to the Brahmaputra, the city did not experience floods. However, human interference has disrupted the natural topography, leading to the current…
Average elevation: 113 m
Narnaul
Narnaul is located at 28°02′N 76°07′E / 28.04°N 76.11°E / 28.04; 76.11. It has an average elevation of 300 meters (977 feet). The district is rich in mineral resources such as iron ore, copper ore, beryl, tourmaline, muscovite, biotite, albite, calcite, and quartz.
Average elevation: 318 m
Laksar
India > Uttarakhand > Laksar
Laksar has an average elevation of 227 metres (745 feet). It is situated between the towns of Khanpur and Sultanpur, and close to the towns of Pathri, Jhabrera and Roorkee in Haridwar district.
Average elevation: 238 m
Lucknow
India > Uttar Pradesh > Lucknow
Lucknow stands at an elevation of approximately 123 metres (404 ft) above sea level. The city had an area of 402 km2 (155 square miles) until December 2019, when 88 villages were added to the municipal limits and the area increased to 631 km2 (244 square miles). Bounded on the east by Barabanki, on the west by…
Average elevation: 120 m
Krishnarajanagara
India > Karnataka > Krishnarajanagara taluk
Krishnarajanagara is located on the northern part of Mysore district, west of the Krishna Raja Sagara Reservoir. It has an average elevation of 786 metres above sea level. NH-373, also known as SH-57 passes through the town of K.R.Nagara.
Average elevation: 786 m
Kharagpur
India > West Bengal > Kharagpur-I
Kharagpur is the fourth largest city of West Bengal in area after Kolkata, Durgapur and Asansol. It is also the fifth most populated city of West Bengal after Kolkata, Asansol, Siliguri, Durgapur - located at 22°19′49″N 87°19′25″E / 22.330239°N 87.323653°E / 22.330239; 87.323653, covering…
Average elevation: 39 m
Rupnagar
India > Punjab > Rupnagar Tahsil
Rupnagar is located at 30°58′N 76°32′E / 30.97°N 76.53°E / 30.97; 76.53. It has an average elevation of 260 metres (850 ft). The town lies on the bank of Satluj River and the Shivalik hill range spreads along the opposite bank of the river.
Average elevation: 281 m
Ujjain
India > Madhya Pradesh > Ujjain NagarTahsil
Ujjain is located in the west-central part of India, and is north of the upper limit of the Vindhya mountain ranges. Located on the Malwa plateau, it is higher than the north Indian plains and the land rises towards the Vindhya Range to the south. Ujjain's coordinates are 23°10′N 75°46′E /…
Average elevation: 501 m
Khandwa
India > Madhya Pradesh > Khandwa Nagar Tahsil
Khandwa is located at 21°50′N 76°20′E / 21.83°N 76.33°E / 21.83; 76.33. It has an average elevation of 313 metres (1026 feet).
Average elevation: 325 m
Amarnath Cave Temple
India > Jammu and Kashmir > Pahalgam
Amarnath Temple is a Hindu shrine located in the Pahalgam tehsil of the Anantnag district of Jammu and Kashmir, India. It is a cave situated at an altitude of 3,888 m (12,756 ft), about 168 km from Anantnag city, the district headquarters, 141 km (88 mi) from Srinagar, the summer capital of Jammu and Kashmir,…
Average elevation: 4,325 m
Chennai
Chennai is located on the south–eastern coast of India in the north–eastern part of Tamil Nadu on a flat coastal plain known as the Eastern Coastal Plains. Its average elevation is around 6.7 metres (22 ft), and its highest point is 60 m (200 ft). Chennai is 2,184 kilometres (1,357 mi) south of Delhi,…
Average elevation: 7 m
Dankuni
India > West Bengal > Chanditala - II
Located at an elevation of None meters (0 feet) above sea level, city's yearly temperature is 30.28 °C (86.5 °F) and it is 4.31% higher than India's averages. Dankuni typically receives about 150.21 millimeters (5.91 inches) of precipitation and has 150.54 rainy days (41.24% of the time) annually.
Average elevation: 6 m
Mysuru
India > Karnataka > Mysuru taluk
Mysore (/maɪˈsɔːr/ (listen)), officially Mysuru ([ˈmaɪˈsuːɾu] (listen)), is a city in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. Mysore city is geographically located between 12° 18′ 26″ north latitude and 76° 38′ 59″ east longitude. It is located at an altitude of 770 m (2,530 ft)…
Average elevation: 727 m
Visakhapatnam
India > Andhra Pradesh > Visakhapatnam (Urban)
The city is situated between the Eastern Ghats and the Bay of Bengal. The city coordinates lies between 17.7041 N and 83.2977 E. The city's area is 682 km2. The average elevation is 45 metres. Visakhpatnam is situated in Coastal Andhra Region.
Average elevation: 35 m
Indrasan
India > Himachal Pradesh > Lahul
Mount Indrasan is located at an altitude of 6221 metres above sea level in Kullu district, Himachal Pradesh. Mt. Indrasan is considered as the most difficult mountain to climb in the Pir Panjal range of the Himalayas because of the challenges involved in scaling it. It was first climbed on October 13, 1962, by…
Average elevation: 5,374 m
Panaji
Panaji was annexed by India with the rest of Goa and the former Portuguese territories after the Indian annexation of Portuguese India in 1961. It became a state-capital on Goa's elevation to statehood in 1987and between 1961 and 1987, it was the capital of the Union Territory of Goa, Daman and Diu. A new…
Average elevation: 19 m
Thiruvilliputtur state assembly constituency
India > Tamil Nadu > Srivilliputhur
Average elevation: 321 m
Kadiri
India > Andhra Pradesh > Kadiri
Kadiri is located at 78.170 degrees E longitude and 14.120 degrees N latitude and has an average elevation of 504.00 meters (1653 feet) above MSL. Kadiri is surrounded by hill on the north and east.
Average elevation: 550 m
