Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
South Dakota topographic map
Click on the map to display elevation.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
South Dakota
Black Elk Peak, formerly named Harney Peak, with an elevation of 7,242 ft (2,207 m), is the state's highest point, while the shoreline of Big Stone Lake is the lowest, with an elevation of 966 ft (294 m). South Dakota is bordered to the north by North Dakota; to the south by Nebraska; to the east by Iowa and Minnesota; and to the west by Wyoming and Montana. The geographical center of the U.S. is 17 miles (27 km) west of Castle Rock in Butte County. The North American continental pole of inaccessibility is between Allen and Kyle, 1,024 mi (1,648 km) from the nearest coastline.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
About this map
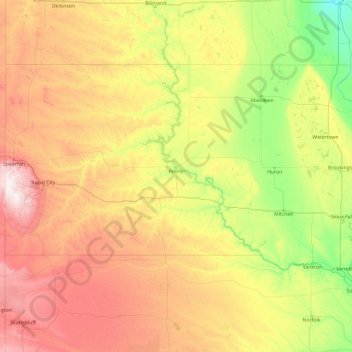
Name: South Dakota topographic map, elevation, terrain.
Location: South Dakota, United States (42.47989 -104.05776 45.94534 -96.43634)
Average elevation: 717 m
Minimum elevation: 274 m
Maximum elevation: 2,166 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Other topographic maps
Click on a map to view its topography, its elevation and its terrain.
Vinings
United States > Georgia > Cobb County
Vinings features a varied topography characterized by rolling hills and lush, wooded areas that provide a picturesque backdrop to the community. The area is nestled alongside the Chattahoochee River, which contributes to the gentle slopes and valleys that define the landscape. Elevations in Vinings typically…
Average elevation: 281 m
Baltimore
United States > Maryland > Baltimore
Baltimore is in north-central Maryland on the Patapsco River close to where it empties into the Chesapeake Bay. The city is also located on the fall line between the Piedmont Plateau and the Atlantic coastal plain, which divides Baltimore into "lower city" and "upper city". The city's elevation ranges from sea…
Average elevation: 65 m
Appalachian Mountains
United States > North Carolina > Yancey County
The Appalachian Mountains (French: Appalaches), often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky…
Average elevation: 1,463 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Ponte Vedra Beach
United States > Florida > Saint Johns County > Ponte Vedra Beach
Ponte Vedra Beach is characterized by its gently rolling terrain that is primarily flat and lies only about 15 feet above sea level. The landscape is predominantly shaped by coastal dunes and the proximity to the Atlantic Ocean, resulting in sandy beaches interspersed with vegetation typical of barrier island…
Average elevation: 3 m
Columbus
United States > Ohio > Franklin County > Columbus
The confluence of the Scioto and Olentangy rivers is just north-west of Downtown Columbus. Several smaller tributaries course through the Columbus metropolitan area, including Alum Creek, Big Walnut Creek, and Darby Creek. Columbus is considered to have relatively flat topography thanks to a large glacier that…
Average elevation: 255 m
Appalachian Mountains
United States > North Carolina > Yancey County
The Appalachian Mountains (French: Appalaches), often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky…
Average elevation: 1,463 m
Virginia Beach
United States > Virginia > Virginia Beach
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 497 square miles (1,290 km2), of which 249 square miles (640 km2) is land and 248 square miles (640 km2) (49.9%) is water. It is the largest city in Virginia by total area and third-largest city land area. The average elevation is 12…
Average elevation: 2 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Indianapolis
United States > Indiana > Indianapolis
Indianapolis is within the Tipton Till Plain, a flat to gently sloping terrain underlain by glacial deposits known as till. The lowest point in the city is about 650 feet (198 m) above mean sea level, with the highest natural elevation at about 900 feet (274 m) above sea level. Few hills or short ridges, known…
Average elevation: 241 m
East Texas
United States > Pennsylvania > Lehigh County > Lower Macungie Township
Average elevation: 126 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Santa Cruz Mountains
United States > California > Santa Clara County
The Santa Cruz Mountains are a region of great biological diversity, encompassing cool, moist coastal ecosystems as well as warm, dry chaparral. Much of the area in the Santa Cruz mountains is considered temperate rainforest. In valleys and moist ocean-facing slopes some of the southernmost coast redwoods…
Average elevation: 230 m
Scottsdale
United States > Arizona > Maricopa County > Scottsdale
The city is in the Salt River Valley, or the "Valley of the Sun," in the northern reaches of the Sonoran Desert. Scottsdale, 31 mi (50 km) long and 11.4 mi (18.3 km) wide at its widest point, shares boundaries with many other municipalities and entities. On the west, Scottsdale is bordered by Phoenix, Paradise…
Average elevation: 414 m
Mount Hood
United States > Oregon > Hood River County
Timberline Lodge is a National Historic Landmark located on the southern flank of Mount Hood just below Palmer Glacier, with an elevation of about 6,000 ft (1,800 m).
Average elevation: 2,716 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Rocky Mountains
United States > Wyoming > Teton County
Agriculture and forestry are major industries. Agriculture includes dryland and irrigated farming and livestock grazing. Livestock are frequently moved between high-elevation summer pastures and low-elevation winter pastures, a practice known as transhumance.
Average elevation: 2,292 m
Navarre
United States > Florida > Santa Rosa County
Navarre is located at 30°24′04″N 86°51′47″W / 30.401°N 86.863°W / 30.401; -86.863Coordinates: 30°24′04″N 86°51′47″W / 30.401°N 86.863°W / 30.401; -86.863. It is located within a portion of the Florida Panhandle observing the Central Time Zone. Elevation is at an average of 10 feet (3.0 m).
Average elevation: 4 m
Grand Canyon
United States > Arizona > Coconino County
Uplift associated with mountain formation later moved these sediments thousands of feet upward and created the Colorado Plateau. The higher elevation has also resulted in greater precipitation in the Colorado River drainage area, but not enough to change the Grand Canyon area from being semi-arid. The uplift…
Average elevation: 1,023 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
San Francisco Bay Area
United States > California > San Francisco
The San Francisco Bay Area is characterized by a diverse and dynamic topography shaped by geological processes over millions of years. This region features a combination of coastal plains, steep hills, and rugged mountains, all influenced by the tectonic activity associated with the nearby San Andreas Fault…
Average elevation: 113 m
Port Charlotte
United States > Florida > Charlotte County
Port Charlotte is characterized by a predominantly flat and low-lying terrain, typical of Florida’s coastal landscape. The area features a network of waterways, including the Peace River and Charlotte Harbor, which provide ample opportunities for recreational activities like boating and fishing. Elevations…
Average elevation: 4 m
Central Park
United States > New York > New York County > New York
In June 1856, Fernando Wood appointed a "consulting board" of seven people, headed by author Washington Irving, to inspire public confidence in the proposed development. Wood hired military engineer Egbert Ludovicus Viele as the park's chief engineer, tasking him with a topographical survey of the site. The…
Average elevation: 26 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Little Saint James Island
United States > United States Virgin Islands > Saint Thomas - Saint John District
Average elevation: 1 m
Saint Peters
United States > Pennsylvania > Chester County > Warwick Township
Average elevation: 157 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Englewood
United States > Wisconsin > Columbia County > Town of Fountain Prairie
Average elevation: 276 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Cameron Park
United States > California > El Dorado County
Cameron Park is situated in an interior chaparral zone or brush zone just east of the Central Valley. It is the closest population center to the Pine Hill Ecological Reserve. Native vegetation includes an abundance of redbud and manzanita bushes, and brush in general. Where treed the native trees are primarily…
Average elevation: 390 m
Vail
United States > Colorado > Eagle County
Vail's average elevation is 8,150 feet (2484 m) above sea level. The town has a total area of 4.5 square miles (12 km2), with no lakes (there is, however, at least one pond). Gore Creek flows from east to west through the center of town.
Average elevation: 2,953 m
Ramona
United States > California > San Diego County
In January 2006, Ramona Valley was designated the country's 162nd American Viticultural Area (AVA) by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau, which recognized the area for its distinctive microclimate, elevation, and soil attributes.
Average elevation: 469 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Palm Harbor
United States > Florida > Pinellas County
Palm Harbor is characterized by its unique topography, which features a relatively rare hilly landscape for the region. Unlike much of the surrounding areas in Pinellas County, which are predominantly flat, Palm Harbor includes elevations that can reach up to about 75 feet above sea level. This elevation gives…
Average elevation: 9 m
Evergreen
United States > Colorado > Jefferson County
Evergreen sits at an elevation of 7,220 feet (2,200 m) in the Rocky Mountains, 19 miles west of Denver, Colorado. Its addresses are oriented according to the Street_system_of_Denver.
Average elevation: 2,309 m
Roosevelt Beach Conservation Area
United States > Washington > Grays Harbor County > Ocean Grove
Average elevation: 18 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Medley Lakeside Retirement Community
United States > Florida > Miami-Dade County > Medley
Average elevation: 6 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
San Diego
United States > California > San Diego County > San Diego
The climate in San Diego, like most of Southern California, often varies significantly over short geographical distances, resulting in microclimates. In San Diego, this is mostly because of the city's topography (the Bay, and the numerous hills, mountains, and canyons). Frequently, particularly during the "May…
Average elevation: 57 m
Jacksonville
United States > Florida > Duval County > Jacksonville
Just south of Jacksonville and north of Saint Augustine is the boundary of where the Floridian Peninsula ends and Continental North America begins; Jacksonville is north of that line. While still in the North American Coastal plain, the topography begins to take on slight Piedmont characteristics. Like the…
Average elevation: 9 m
Point Reyes
United States > California > Marin County
Point Reyes is bounded to the east by the San Andreas Fault, which runs directly under Tomales Bay, and is structurally dominated by the Point Reyes Syncline. The Point Reyes Peninsula is on the Pacific Plate, while the rest of Marin County land is on the North American Plate. The peninsula is a member of the…
Average elevation: 10 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Blue Diamond
United States > Nevada > Clark County
Blue Diamond is the site of Cottonwood Spring (formerly known as Ojo de Cayetana, or Pearl Spring), a watering place and campsite on the Old Spanish Trail and the later Mormon Road between Mountain Springs and Las Vegas Springs. The springs are located on a mountainside south of the town at 36°02′44″N…
Average elevation: 1,106 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Atlanta
United States > Georgia > Fulton County
Atlanta (/ætˈlæntə/ at-LAN-tə) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is the seat of Fulton County, the most populous county in Georgia. With a population of 498,715 living within the city limits, it is the eighth most populous city in the Southeast and 38th most populous…
Average elevation: 285 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Blue Ridge Mountains
United States > Virginia > Botetourt County
Although the term "Blue Ridge" is sometimes applied exclusively to the eastern edge or front range of the Appalachian Mountains, the geological definition of the Blue Ridge province extends westward to the Ridge and Valley area, encompassing the Great Smoky Mountains, the Great Balsams, the Roans, the Blacks,…
Average elevation: 460 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Hopeland
United States > Pennsylvania > Lancaster County > Clay Township > Clay
Average elevation: 155 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Grand Canyon
United States > Arizona > Coconino County
Uplift associated with mountain formation later moved these sediments thousands of feet upward and created the Colorado Plateau. The higher elevation has also resulted in greater precipitation in the Colorado River drainage area, but not enough to change the Grand Canyon area from being semi-arid. The uplift…
Average elevation: 1,023 m
Yellow Creek
United States > Pennsylvania > Bedford County > Hopewell Township > Yellow Creek
Average elevation: 323 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Palolo Valley Recreational Park
United States > Hawaii > Honolulu County > East Honolulu
Average elevation: 144 m
Little Diomede Island
United States > Alaska > Unorganized Borough > Diomede > Diomede
Average elevation: 160 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Boston
United States > Massachusetts > Suffolk County > Boston
Boston has an area of 89.63 sq mi (232.1 km2)—48.4 sq mi (125.4 km2) (54%) of land and41.2 sq mi (106.7 km2) (46%) of water. The city's official elevation, as measured at Logan International Airport, is 19 ft (5.8 m) above sea level. The highest point in Boston is Bellevue Hill at 330 ft (100 m) above sea…
Average elevation: 26 m
El Dorado Hills
United States > California > El Dorado County > Cameron Park
El Dorado Hills (EDH), as defined by the 2010 census-designated place (CDP), is at the western border of El Dorado County, between the City of Folsom and the unincorporated community of Cameron Park. The northern limits of the CDP are Folsom Lake and the South Fork of the American River, where river rafters…
Average elevation: 254 m
Tug Hill
United States > New York > Oswego County
The core Tug Hill region encompasses 150,000 acres (610 km2) of unbroken, generally second-growth, northern hardwood forest, and is drained by a vast network of streams. Important rivers and streams whose headwaters are located within the Tug Hill region include the Mohawk River, Deer River, Salmon River, Mad…
Average elevation: 109 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Andover Golf Estates
United States > Florida > Miami-Dade County > Miami Gardens
Average elevation: 7 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
