Acolman topographic map
Interactive map
Click on the map to display elevation.
Acolman
The municipality is located on a plain in the northern portion of the Valley of Mexico called the Valley of Teotihuacan. It has only three significant elevations. The eastern border is marked by the Sierra de Patlachique and the west is marked by a mountain called Chiconautla. Chiconautla and Tlahuilco are forested and are protected areas. From the mountains that surround this plain flow a number of streams such as the San José and the San Antonio, which are commonly called the Rio Grande and the Rio Chico. The municipality lacks fresh water springs, with most potable water coming from deep wells. The climate is temperate and semi-arid with rains in the summer. Temperatures can range from 36 °C in the summer to -4 °C in the winter. Forested areas of the municipality contain trees such as ahuehuete, mesquite, eucalyptus and Peruvian pepper. In the lower, flatter regions, the flora consists of shrubs, grasses, cactus and other plants adapted to dry areas. Wildlife consists mostly of small mammals such as rabbits and skunks, small reptiles such as the chameleon and insects.
About this map
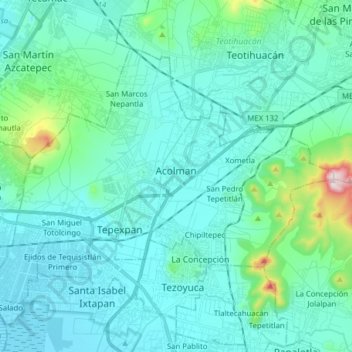
Name: Acolman topographic map, elevation, terrain.
Location: Acolman, State of Mexico, Mexico (19.58332 -98.99723 19.69023 -98.84075)
Average elevation: 2,298 m
Minimum elevation: 2,230 m
Maximum elevation: 2,744 m
Other topographic maps
Click on a map to view its topography, its elevation and its terrain.
Valle de Bravo
Mexico > State of Mexico > Valle de Bravo
The municipality is surrounded by mountain ranges and other elevated areas covering about 50% of the total area and include the Sierra de Temascaltepec, Sierra de Tenayac, Sierra de Valle de Bravos as wells as the hills that roll around the mountain ranges. These elevations include a number of small volcanoes…
Average elevation: 1,914 m
Texcoco de Mora
Mexico > State of Mexico > Texcoco
Tescoco lies about 25 km east of the centre of Mexico City. Major elevations in the municipality include the Tlaloc Mountain (4,500 meters) the Tetzcutzinco, Moyotepec and Tecuachacho. Most elevations are named after the major community to be found on them. There are also a number of small canyons. Part of the…
Average elevation: 2,448 m
Eje Neovolcánico
Mexico > State of Mexico > Amecameca
Volcanic ash make soils in the region very fertile, which (especially coupled with elevation making tropical climate milder) has led to high human population densities in the belt that now sometimes strain the environment.
Average elevation: 4,179 m
Popocatépetl
Mexico > State of Mexico > Atlautla
According to paleomagnetic studies, the volcano is about 730,000 years old. It is cone shaped with a diameter of 25 km (16 mi) at its base, with a peak elevation of 5,450 m (17,880 ft). The crater is elliptical with an orientation northeast-southwest. The walls of the crater vary from 600 to 840 m (1,970 to…
Average elevation: 4,810 m
Santiago Tianguistenco
Mexico > State of Mexico > Tianguistenco
The municipality lies in the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt in the sub-province of the Lakes and Volcanoes of Anahuac. 35% of the municipality is mountainous, 30% is arable and the rest is developed. The topography of the municipality varies due to its size. The eastern portions are highest as they are in the…
Average elevation: 2,645 m
Santa Ana Jilotzingo
Mexico > State of Mexico > Jilotzingo > Santa Ana Jilotzingo
Average elevation: 2,760 m
Ciudad Adolfo Lopez Mateos
Mexico > State of Mexico > Atizapán de Zaragoza > Ciudad Adolfo Lopez Mateos
Its main elevations are Biznaga Hill, Atlaco Hill La Condesa Hill and Grande Hill.
Average elevation: 2,426 m
San Lorenzo Tlalmimilolpan
Mexico > State of Mexico > Teotihuacán > San Lorenzo Tlalmimilolpan
Average elevation: 2,274 m
