La Pampa topographic map
Interactive map
Click on the map to display elevation.
La Pampa
Being located in the Pampas, the province has a cool temperate climate. In general, the province is dominated by two different types of climates: a temperate one in the east and a semi-arid one in the west. Precipitation generally decreases from east to west and from north to south. Being characterized by large thermal amplitudes, the climate of the province has continental characteristics, particularly in the west where thermal amplitudes are much larger. The general atmospheric circulation is one of the most important factors that influence the climate on a regional scale. During summer, the South Atlantic High is displaced to the southeast, which brings hot and humid air masses from the north and northeast. The South Pacific High in summer is responsible for bringing cooler air masses from the southwest which when these two contrasting air masses meet lead to precipitation occurring. In contrast, winters are dry due to the northward displacement of the South Atlantic high and the topographic barrier of the Andes north of 40oS which prevents frontal systems that bring precipitation from reaching the province. Any winds from the southwest during winter bring in cold and dry weather since most of the precipitation and humidity are released in the Andes. As such, most of the precipitation occurs during summer.
About this map
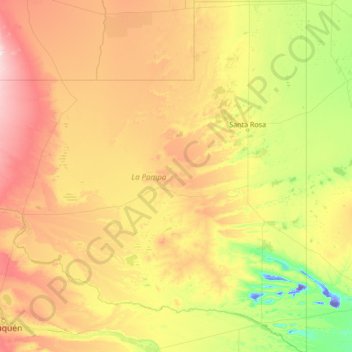
Name: La Pampa topographic map, elevation, terrain.
Location: La Pampa, Argentina (-39.32980 -68.29677 -35.00226 -63.38265)
Average elevation: 262 m
Minimum elevation: -45 m
Maximum elevation: 1,131 m
Other topographic maps
Click on a map to view its topography, its elevation and its terrain.
Andes
The Andes Mountains are the highest mountain range outside Asia. The highest mountain outside Asia, Argentina's Mount Aconcagua, rises to an elevation of about 6,961 m (22,838 ft) above sea level. The peak of Chimborazo in the Ecuadorian Andes is farther from the Earth's center than any other location on the…
Average elevation: 165 m
Río Negro Province
The climate of the province is temperate at low elevations, and very cold in the higher Andean peaks.
Average elevation: 621 m
Junta de Gobierno de Colonia Ensayo
Argentina > Entre Ríos Province > Distrito Salto
Average elevation: 47 m
Mendoza
The area around Malargue is located at higher elevation (1400 meters) and thus the weather is significantly colder: summers average 28 °C (82 °F) during the day, but only 11 °C (53F) at night, and winters range from 10 °C (50 °F) to −2 °C (28 °F). Here, precipitation is somewhat higher (350 mm) and…
Average elevation: 1,069 m
Municipio de San Antonio de los Cobres
The town is known for its high elevation of approximately 3,775 meters (12,385 feet) above sea level, being one of the highest elevations of any city or town in Argentina. It is located approximately 160 kilometers (99 mi) from the city of Salta and 2,000 kilometers (1,200 mi) from the capital, Buenos Aires.…
Average elevation: 3,733 m
Distrito Ciudad de Tunuyán
Tunuyán is a city in the west of the province of Mendoza, Argentina, located on the western shore of the Tunuyán River, 80 km (50 mi) south from the provincial capital Mendoza and 100 km (62 mi) east of the Chilean border. It has 49,132 inhabitants, and is the head town of the Tunuyán Department. Along with…
Average elevation: 877 m
Patagonia
Across much of Patagonia east of the Andes, volcanic eruptions have created formation of basaltic lava plateaus during the Cenozoic. The plateaus are of different ages with the older –of Neogene and Paleogene age– being located at higher elevations than Pleistocene and Holocene lava plateaus and outcrops.
Average elevation: 173 m
Municipio de Villa La Angostura
The elevation of the city centre is about 790 m (2,590 ft), and the lake is at 765 m (2,510 ft). Surrounding mountains range from 1,500 m (4,900 ft) to about 2,000 m (6,600 ft) (Cerro Bayo, right behind the city, is 1,782 m (5,846 ft) high).
Average elevation: 1,037 m
Junta de Gobierno de Gobernador Febre
Argentina > Entre Ríos Province > Distrito Montoya
Average elevation: 62 m
Trevelin
Trevelin has a temperate oceanic climate (Köppen Cfb), but with a rainfall pattern similar to the Mediterranean climate (Köppen Csb). The climate is milder than that of other locations on the Argentine side of Northern Patagonia because of the low altitude and the direct exposure to Pacific winds. This…
Average elevation: 403 m
Monumento Natural del Abra del Acay
The Abra del Acay in La Poma Department, Salta Province, Argentina is the highest point on Argentina's National Route 40. Located at 24°23′S 66°14′W / 24.383°S 66.233°W / -24.383; -66.233, its altitude is 4,972 meters (16,312 ft), even though an old sign informs visitors it stands at 4,895…
Average elevation: 4,291 m
Andes
Argentina > Mendoza > Distrito Las Cuevas
The Andes Mountains are the highest mountain range outside Asia. The highest mountain outside Asia, Argentina's Mount Aconcagua, rises to an elevation of about 6,961 m (22,838 ft) above sea level. The peak of Chimborazo in the Ecuadorian Andes is farther from the Earth's center than any other location on the…
Average elevation: 6,208 m
