Auckland topographic map
Interactive map
Click on the map to display elevation.
Auckland
The Auckland Volcanic Field has contributed greatly to the growth and prosperity of the Auckland Region since the area was settled by humans. Initially, the maunga (scoria cones) were occupied and established as pā (fortified settlements) by Māori due to the strategic advantage their elevation provided in controlling resources and key portages between the Waitematā and Manukau harbours. The rich volcanic soils found in these areas also proved ideal for the cultivation of crops, such as kumara. Following European arrival, many of the maunga were transformed into quarries to supply the growing city with aggregate and building materials, and as a result were severely damaged or entirely destroyed. A number of the smaller maar craters and tuff rings were also removed during earthworks. Most of the remaining volcanic centres are now preserved within recreational reserves administered by Auckland Council, the Department of Conservation, and the Tūpuna Maunga o Tāmaki Makaurau Authority.
About this map
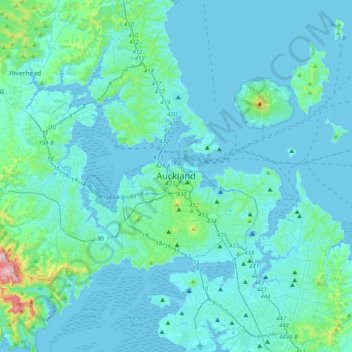
Name: Auckland topographic map, elevation, terrain.
Location: Auckland, Waitematā, Auckland, 1010, New Zealand (-37.01210 174.60318 -36.69210 174.92318)
Average elevation: 32 m
Minimum elevation: -2 m
Maximum elevation: 394 m
Other topographic maps
Click on a map to view its topography, its elevation and its terrain.
Little Barrier Island
New Zealand > Auckland > Aotea Great Barrier
The island is steeply sloping, and deeply dissected by ravines radiating from a central range that peaks at Mount Hauturu whose altitude is 722 m (2,369 ft). Te Titoki Point is the only area of flat land on the island.
Average elevation: 145 m
