Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Sarawak topographic map
Click on the map to display elevation.
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Sarawak
Sarawak can be divided into two geological zones: the Sunda Shield, which extends southwest from the Batang Lupar River (near Sri Aman) and forms the southern tip of Sarawak, and the geosyncline region, which extends northeast to the Batang Lupar River, forming the central and northern regions of Sarawak. The oldest rock type in southern Sarawak is schist formed during the Carboniferous and Lower Permian times, while the youngest igneous rock in this region, andesite, can be found at Sematan. Geological formation of the central and northern regions started during the late Cretaceous period. Other types of stone that can be found in central and northern Sarawak are shale, sandstone, and chert. The Miri Division in eastern Sarawak is the region of Neogene strata containing organic rich rock formations which are the prolific oil and gas reserves. The rocks enriched in organic components are mudstones in Lambir, Miri and Tukau Formations of Middle Miocene-Lower Pliocene age. Significant quantities of Sarawak soil are lithosols, up to 60 per cent, and podsols, around 12 per cent, while abundant alluvial soil is found in coastal and riverine regions. 12 per cent of Sarawak is covered with peat swamp forest. Limestone with well-developed karst topography and cave systems is found scattered from west to east Sarawak, but concentrated in certain regions such as in the Bau district in the west and southwards near the Kalimantan border.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
About this map
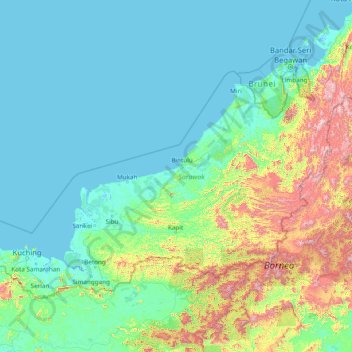
Name: Sarawak topographic map, elevation, terrain.
Location: Sarawak, Malaysia (0.85382 109.53804 5.10833 115.67803)
Average elevation: 228 m
Minimum elevation: -4 m
Maximum elevation: 2,148 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Other topographic maps
Click on a map to view its topography, its elevation and its terrain.
Kuala Lumpur
Located in the centre of Selangor state, Kuala Lumpur was a territory of Selangor State Government. In 1974, Kuala Lumpur was split off from Selangor to form the first Federal Territory governed directly by the Malaysian federal government. Its location in the most developed state on the west coast of…
Average elevation: 127 m
Kampung Sungai Semungkis
Malaysia > Selangor > Kajang Municipal Council > Batu 14 Hulu Langat
Average elevation: 85 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Kuala Terengganu
Malaysia > Terengganu > Kuala Terengganu
As a part of Terengganu, Kuala Terengganu has a tropical rainforest climate under the Köppen climate classification (Af) with constant temperature and high humidity. The amount of rainfall varies according to the monsoon season. It is generally fairly hot and humid all year round, averaging from 28 °C to 30…
Average elevation: 9 m
Sibu
Sibu is located near the Rajang delta at the confluence of Rajang and Igan rivers. Peat swamp forests and alluvial plains are particularly prevalent in the Sibu Division. Sibu is located on a deep peat soil, which has caused problems in infrastructure development because buildings and roads slowly sink into…
Average elevation: 10 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Penang Island
Penang Island is irregularly shaped, with a hilly and mostly forested interior; its coastal plains are narrow, the most extensive of which is at the northeastern cape. With a height of 833 m (2,733 ft), Penang Hill, at the centre of the island, is the tallest point within Penang. From a small settlement at the…
Average elevation: 117 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Cameron Highlands
Surveyed by the government geologist and explorer William Cameron in 1885, the outpost consists of three mukims (subdistricts), namely Ringlet, Tanah Rata and Ulu Telom. Its eight settlements are Ringlet, Tanah Rata (the administrative centre), Brinchang, the Bertam Valley, Kea Farm, Tringkap, Kampung Kuala…
Average elevation: 1,400 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Pahang
The highest peak, Mount Tahan, reaches 2,187 m (7,175 ft) in elevation, which is also the highest point in the Peninsular Malaysia. The climate is temperate enough to have distinct temperature variations year round, and much of the highlands are covered with tropical rainforest. Pahang is home to Malaysia's…
Average elevation: 90 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Mount Kinabalu
Low's Peak can be climbed by a person in good physical condition without mountaineering equipment on the main route. However, climbers must be accompanied by accredited guides at all times due to national park regulations and the risk of experiencing altitude sickness.
Average elevation: 3,567 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Mount Kinabalu
Mount Kinabalu (Malay: Gunung Kinabalu, Dusun: Gayo Ngaran or Nulu Nabalu) is the highest mountain in Borneo and Malaysia. With an elevation of 13,435 feet (4,095 m), it is third-highest peak of an island on Earth, and 20th most prominent mountain in the world by topographic prominence. The mountain is located…
Average elevation: 3,567 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Seri Iskandar
Seri Iskandar (Jawi: سري إسكندر, Chinese: 斯里依斯干达) is a major town within the Perak Tengah District in the state of Perak, Malaysia. It is situated about 40 kilometers southwest of the city of Ipoh, the state capital. The town is at an average elevation of 29 meters above the sea level. The…
Average elevation: 29 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
