Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Mexico City topographic map
Click on the map to display elevation.
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Mexico City
Mexico is crossed from north to south by two mountain ranges known as Sierra Madre Oriental and Sierra Madre Occidental, which are the extension of the Rocky Mountains from northern North America. From east to west at the center, the country is crossed by the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt also known as the Sierra Nevada. A fourth mountain range, the Sierra Madre del Sur, runs from Michoacán to Oaxaca. As such, the majority of the Mexican central and northern territories are located at high altitudes, and the highest elevations are found at the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt: Pico de Orizaba (5,700 m or 18,701 ft), Popocatépetl (5,462 m or 17,920 ft) and Iztaccihuatl (5,286 m or 17,343 ft) and the Nevado de Toluca (4,577 m or 15,016 ft). Three major urban agglomerations are located in the valleys between these four elevations: Toluca, Greater Mexico City and Puebla. An important geologic feature of the Yucatán peninsula is the Chicxulub crater. The scientific consensus is that the Chicxulub impactor was responsible for the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. Mexico is subject to a number of natural hazards, including hurricanes on both coasts, tsunamis on the Pacific coast, and volcanism.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
About this map
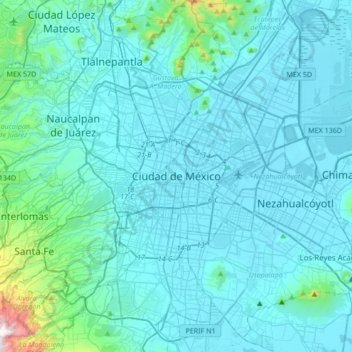
Name: Mexico City topographic map, elevation, terrain.
Location: Mexico City, 06060, Mexico (19.27263 -99.29318 19.59263 -98.97318)
Average elevation: 2,321 m
Minimum elevation: 2,223 m
Maximum elevation: 3,510 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Other topographic maps
Click on a map to view its topography, its elevation and its terrain.
Cozumel
Large parts of the island are covered with mangrove forest which has many endemic animal species. Cozumel is a flat island based on limestone, resulting in a karst topography. The highest natural point on the island is less than 15 m (49 ft) above sea level. The cenotes are deep water-filled sinkholes formed…
Average elevation: 1 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Parque Nacional Huatulco
Mexico > Oaxaca > Santa María Huatulco > Bahía de Conejos
Average elevation: 9 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Tenancingo
The seat of the municipality is the town of Tenancingo, surrounded by mountains and forest. The main elevation overlooking the town is the Cerro de las Tres Marías, topped by a giant white statue of Christ the King (Cristo Rey), built in 1985, designed by Hector Morret and visible from just about anywhere in…
Average elevation: 2,053 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Villa Sola de Vega
The municipality covers an area of 680 km2 (260 sq mi). The municipal seat is at an elevation of 1,440 m (4,720 ft). Average temperature is 18 °C (64 °F) and average rainfall is 950ml per year. The Sola River runs through the municipality, a tributary of the Atoyac River.
Average elevation: 1,685 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Huasca de Ocampo
The municipality extends from the Sierra de Pachuca mountains, where the town is, to over part of a wide, flat valley with lower altitude and warmer temperatures. This area is filled with small towns and villages, as well as fields and orchards. The higher elevations around these flat lands are forested with…
Average elevation: 2,208 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Las Sendas
Mexico > Nuevo León > San Pedro Garza García > Zona Valle Poniente
Average elevation: 720 m
Parque Estatal Manantial de la Media Luna
Mexico > San Luis Potosi > Rioverde
Average elevation: 1,006 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
La Magdalena Contreras
La Magdalena Contreras (Spanish pronunciation: [maɣðaˈlena konˈtɾeɾas] ) is a borough (demarcación territorial) in the Mexico City. As of the 2010 census, it has a population of 239,086 inhabitants and is the third-least populous of Mexico City's boroughs. It lies at an elevation of 2,365 m (7,759 ft)…
Average elevation: 2,828 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Tepehuanes
Tepehuanes is a municipality in the Mexican state of Durango. It is located in the North West of Durango at 25°12'"-26°25'"N 105°23'"-106°40'"W, at an elevation of about 1,830 meters (6000 feet).
Average elevation: 2,234 m
Cedros Island
Mexico > Baja California > Municipio de Ensenada
Cedros Island (Isla de Cedros, "island of cedars" in Spanish) is an island in the Pacific Ocean belonging to the state of Baja California, Mexico. The dry and rocky island had a population of 1,350 in 2005 and has an area of 348 square kilometres (134 sq mi) which includes the area of several small nearby…
Average elevation: 67 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Durango
With 123,451.2 km2 or 12.3 million ha, Durango accounts for about 6.3% of the entire territory of Mexico. It is the fourth largest state lying at the extreme northwest of the Central Mexican Plateau, where it meets the Sierra Madre Occidental—the highest peaks in the state. The state has an average elevation…
Average elevation: 1,954 m
Ruiz
The area of the municipality extends from the western lowlands to the foothills of the Sierra Madre Occidental. About 70% of its surface is made up of rugged lands. The municipal seat is located on the coastal plain at an elevation of 30 meters above sea level. It is here where the agricultural lands are…
Average elevation: 623 m
Arandas
Arandas is situated on the Mesa Central at an elevation of 6,762 feet (2,061 metres). Arandas is commonly known among Mexicans as the commercial and manufacturing centre for agricultural products (typically beans and wheat) and its pastoral environment, which allows the city to produce various commercial…
Average elevation: 2,031 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Isla Cozumel
Mexico > Quintana Roo > Cozumel
Large parts of the island are covered with mangrove forest which has many endemic animal species. Cozumel is a flat island based on limestone, resulting in a karst topography. The highest natural point on the island is less than 15 m (49 ft) above sea level. The cenotes are water-filled sinkholes formed by…
Average elevation: 2 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Atlacomulco
The municipality has rugged terrain, filled with mountains and hills. It is located on the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt, in the Lakes and Volcanos of Anáhuac region. Principle elevations include Cerro Xitije, Cerro Atlacomulco, Cerro La Cruz and Cerro El Cielito. Its altitude varies from 2720 to 3030 meters…
Average elevation: 2,665 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Tulancingo de Bravo
It is located in the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt in the Sierra Hidalgo, as it begins its descent to the Gulf of Mexico. It is mostly valley floor with some peaks. This relatively flat surface is mostly of light volcanic rock cut with ravines, small canyons, large hills and volcanoes. The larger canyons include…
Average elevation: 2,242 m
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Make a donation
Gear up for your next adventure:
As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
